Last Updated: July 2025
In today’s competitive digital landscape, understanding consumer behavior is key to crafting personalized marketing strategies. Behavioral marketing examples show how businesses categorize customers based on their interactions, purchasing habits, and engagement levels, leading to more targeted and effective campaigns.
In fact, 91% of consumers are more likely to shop with brands that provide relevant offers and recommendations (Accenture). By leveraging behavioral segmentation, companies can enhance customer experience, boost retention rates, and maximize conversions.
In this article, we’ll define behavioral marketing segmentation and explore seven impactful behavioral marketing examples to illustrate its effectiveness.
Understanding Behavioral Marketing Segmentation
Behavioral marketing segmentation groups consumers based on how they interact with and engage with a company. This method assesses common behavioral characteristics, for instance, knowledge, attitudes, preferences, what they use, and their responses to products, services, promotions, or brands.
Key Objectives of Behavioral Segmentation
- Identifying Customer Needs: Adjusting to the unique needs and preferences of various customer segments with a clear focus.
- Personalizing Offerings: Adjusting products or services based on consumer habits.
- Optimizing the Buyer’s Journey: Improving customer experience with a smooth buying experience.
- Assessing Customer Value: Establishing potential worth to help retain and enhance profits.
- Developing Targeted Marketing Strategies: Expanding and retaining the customer base with data-driven insights.
Behavioral vs. Demographic Segmentation
Focusing on who they are based on age, gender, income, and location is a demographic segmentation to group consumers. Let’s say a luxury car brand targets high-income people between the ages of 35-55.
Behavioral segmentation, on the other hand, looks at what customers do. It examines purchase habits, brand loyalty, and engagement. For example, an e-commerce brand might discount people who regularly abandon carts.

The fact is that 80% of consumers are more likely to purchase from brands that personalize and target experiences based on their behavior.
Demographic information gives you a very wide-picture view of your audience, while behavioral data provides a more individualized approach to marketing. Top strategies use both for more targeted messaging and higher conversions.
Key Advantages of Behavioral Targeting
By segmenting a market into smaller, well-defined variables, brands can better devote time and resources. Using the same marketing approach for everyone will only appeal to a small segment of consumers, which can significantly dilute its effectiveness.
From exploring your target audience down to segmenting them, businesses can execute personalized advertising for a higher consumer feel and resolve them through their very own demands.
- Personalization – Customizing and optimizing offers according to timing and preferred channels improves customer engagement and guides customers in their buying process.
- Predictive Insights – Predicting future customer actions is possible by applying historical behavioral patterns to inform proactive marketing initiatives.
- Prioritization – Finding high-value prospects helps strategize time, budget, and resources to drive business impact at scale.
- Performance Tracking – As segment growth and behavioral shifts expand over time, you may dive more deeply into understanding how healthy key segments are and how effective your marketing efforts have been.
Variables of Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation focuses on segmenting customers according to their behavior and interaction with a particular brand. This helps businesses create data-driven and strategic marketing strategies that constantly push conversions.
1. Purchase Behavior
This variable concerns itself with fandom by customers they relate to the products, the price, actions for buying, low-volume or high-volume, or brand preference, etc. It enables businesses to analyze loyal purchasers, casual visitors, and budget-conscious buyers.
2. Usage Behavior
Customers are grouped according to the frequency and extent of product or service usage. It allows businesses to customize and personalize their services, experiences, and retention plans.
3. Customer Loyalty and Retention
It helps brands understand the difference between a high-value customer and one who could be on the brink of churning. This variable is leveraged by businesses to create their reward programs & personalized engagement strategies.
4. Engagement Levels
This variable tracks customer interactions across multiple channels, including website visits, email engagement, and social media activity. It enables brands to sharpen their communication techniques and enhance conversion rates.
5. Benefits Sought
The importance of different product features varies for different customers. This helps businesses to offer the right stuff and create the right messages.
Behavioral Marketing Examples
Using Behavioral marketing segmentation, companies can tailor their strategies according to user behavior, interests, and engagement. According to research, personalized marketing can boost conversion rates by 202%.

Insights from consumer behavior can create hyper-targeted marketing campaigns that improve brand loyalty and increase sales. Here are seven major types of behavioral marketing segmentation, plus real-life examples.
1. Purchase Behavior Segmentation
Segmentation based on purchase behavior involves classifying customers with respect to their purchasing pattern, i.e., the number of their purchases, the sum spent and their response to a discount offer, etc. Businesses can use these clusters to form targeted marketing tactics for various groups of customers.
For instance, an online brand can present a new visitor with an introductory discount, and longtime customers with extra loyalty benefits or early access to curated collections.
By segmenting their customer base, brands can more effectively optimize their pricing strategies, promotions, and product recommendations to drive more frequent and higher-value purchases.
2. Usage-Based Segmentation
Usage-based segmentation assesses both the frequency and volume of customers’ use of a product or service. Companies use this data to customize their marketing accordingly.
For example, Netflix and Spotify recommend personalized content based on user’s previous activity to maintain ongoing access and interest. Just like software companies segment their users into “light”, “moderate” and “heavy” and release features or retention strategies based on the usage profile. It helps companies improve customer satisfaction and reduce churn.
3. User Status Segmentation
User status segmentation categorizes customers based on their relationship with the brand (e.g. new users, active users, inactive users, potential customers, etc.). It calls for a distinct marketing strategy for each group.
Let’s say a SaaS Company sends Onboarding Emails with tutorials to their new users and offers special discounts or re-engagement campaigns to their inactive users.
This segmentation guarantees that customers at various lifecycle stages are engaged in relevant communication for retention and continued lifetime value.
4. Engagement-Based Segmentation
Customers engage with brands at different levels so segmenting them based on how engaged they are helps organizations frame their messages to them effectively. Varying levels might involve regular updates and exclusive content for those users who are highly engaged. Whereas if you have a disengaged user, you may want to have some reconnection efforts.
So, for example, a fashion retailer might send weekly emails to their most engaged subscribers and a few reminders about continuing sales to their more casual users.
Brands can leverage engagement levels to fine-tune their marketing cadence and creativity to keep customers engaged.
5. Loyalty-Based Segmentation
Loyalty-based segmentation identifies repeat customers and rewards them to foster brand loyalty over time. Many companies create loyalty programs to keep the high-value customer.
Starbucks Rewards Program is an example of this, where points are awarded to each purchase made and redeemed for free drinks and special offers.
By dividing customers into groups based on their loyalty, brands can create customized incentives, allowing the relationships with their customers to husbands and their lifetime value.
6. Time-Based Segmentation
Time factors such as time of the year (seasonality), time of the day, and frequency of interactions can all impact customer behavior. For instance, businesses can segment customers by time. This can aid in optimizing marketing campaigns by targeting customers at the right time.
Retailers, for example, advertise back-to-school sales in late summer and holiday shopping offers in November and December. Food delivery apps, on the other hand, send lunchtime and dinnertime promotions to entice their users to order in.
Knowing when customers are most likely to engage allows brands to unlock the full potential of their marketing efforts.
7. Benefit-Based Segmentation
Benefit-based segmentation defines a group of customers based on the specific value or the benefit a customer is looking to get from a product or service. This way, it aligns your marketing messages with customers’ unique needs.
For instance, a skincare company may divide customers based on anti-ageing, acne, or moisture concerns and provide recommendations based on the type of product they are looking for.
This level of personalization makes customers happier and helps to convert them into actual sales. In industries with diverse consumer needs, such as beauty, fitness, and healthcare, benefit-based segmentation works quite well.
Saufter: Best Personalized Email Marketing Automation Software

Saufter is a rich customer engagement and email marketing platform that tracks user behavior on your website or portal. It provides intelligent recommendations to drive engagement by tracking user journey stages.
For example, if a user has not used a specific feature, Saufter may recommend a related “how-to” article. Each week, it offers fully written email and in-app campaigns, requiring just your signoff and go-ahead.
Moreover, Saufter keeps a watch on your competitors, finding trending content from their recent blogs and suggesting content campaigns that can really help in your strategy.

And when behavioral targeted emails have a 147% higher click-through rate, Saufter provides your marketing efforts with data-based decisions.
Key Automation Features Include:
- Automatically segmenting users into cohorts based on their behavior.
- Email campaign recommendations powered by AI to maximize conversions and minimize churn.
- Automated recommendations for SEO campaigns.
- Forecasting conversion rates and fraud prevention.
Conclusion
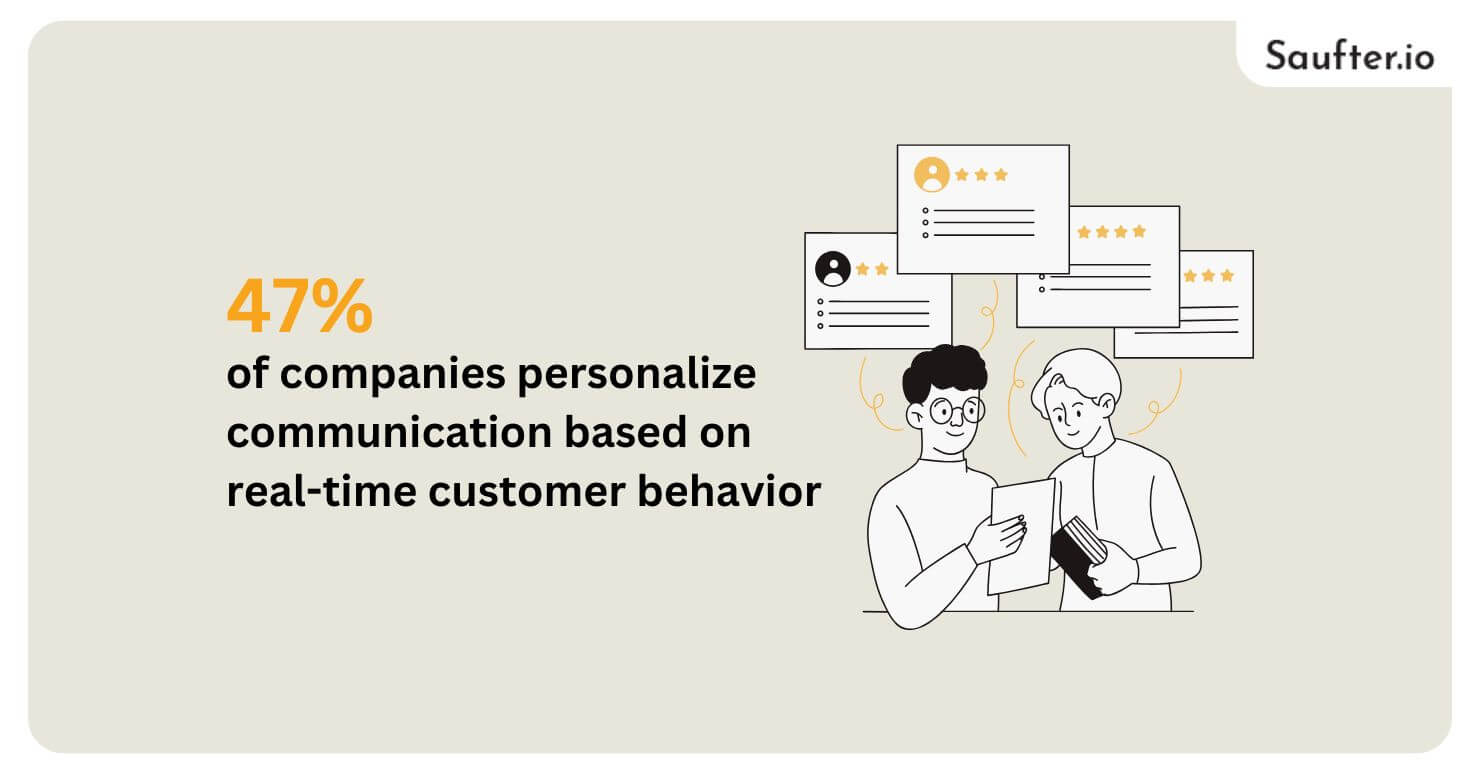
In today’s competitive landscape, behavioral marketing examples demonstrate the power of segmentation in creating personalized customer experiences. By understanding how users interact with your brand, you can craft targeted campaigns that drive engagement and conversions. In fact, 47% of companies personalize communication based on real-time customer behavior, emphasizing the need for data-driven marketing strategies.
Platforms like Saufter take behavioral segmentation to the next level by automating user tracking, campaign recommendations, and competitive insights. Whether it’s segmenting users based on engagement, purchase history, or in-app behavior, Saufter ensures your marketing efforts align with the best behavioral marketing examples for maximum impact.
Start leveraging behavioral segmentation today and gain a competitive edge!

















